

Cryogenic vaporizers are essential devices used to convert cryogenic liquids—such as liquid nitrogen (LIN), liquid oxygen (LOX), liquid argon (LAr), and liquefied natural gas (LNG)—into their gaseous forms by adding controlled heat. These gases are stored at extremely low temperatures to maintain their liquid phase, but most industrial processes require them in gaseous form with stable pressure, precise flow rates, and high purity. Vaporizers achieve this transformation by transferring heat through several methods, including ambient air convection, steam or hot water systems, and electrically heated elements.
The fundamental purpose of a cryogenic vaporizer is to safely and efficiently supply gas on demand, ensuring that downstream systems—from medical oxygen networks and food freezing lines to semiconductor fabrication and LNG regasification—receive a consistent and reliable gas output. Each vaporizer type offers distinct advantages in terms of energy efficiency, response time, cost, and suitability for different climates and installation environments.
Understanding how these vaporizers operate, the components involved, and the engineering principles behind heat transfer and phase change is crucial for industries that depend on uninterrupted gas supply. This guide provides an in-depth explanation of vaporizer mechanisms, structural design considerations, vaporizer classifications, standard applications, and safety requirements. It also highlights how CryoTech’s advanced vaporizer solutions are engineered to deliver exceptional performance, long-term reliability, and compliance with international standards.
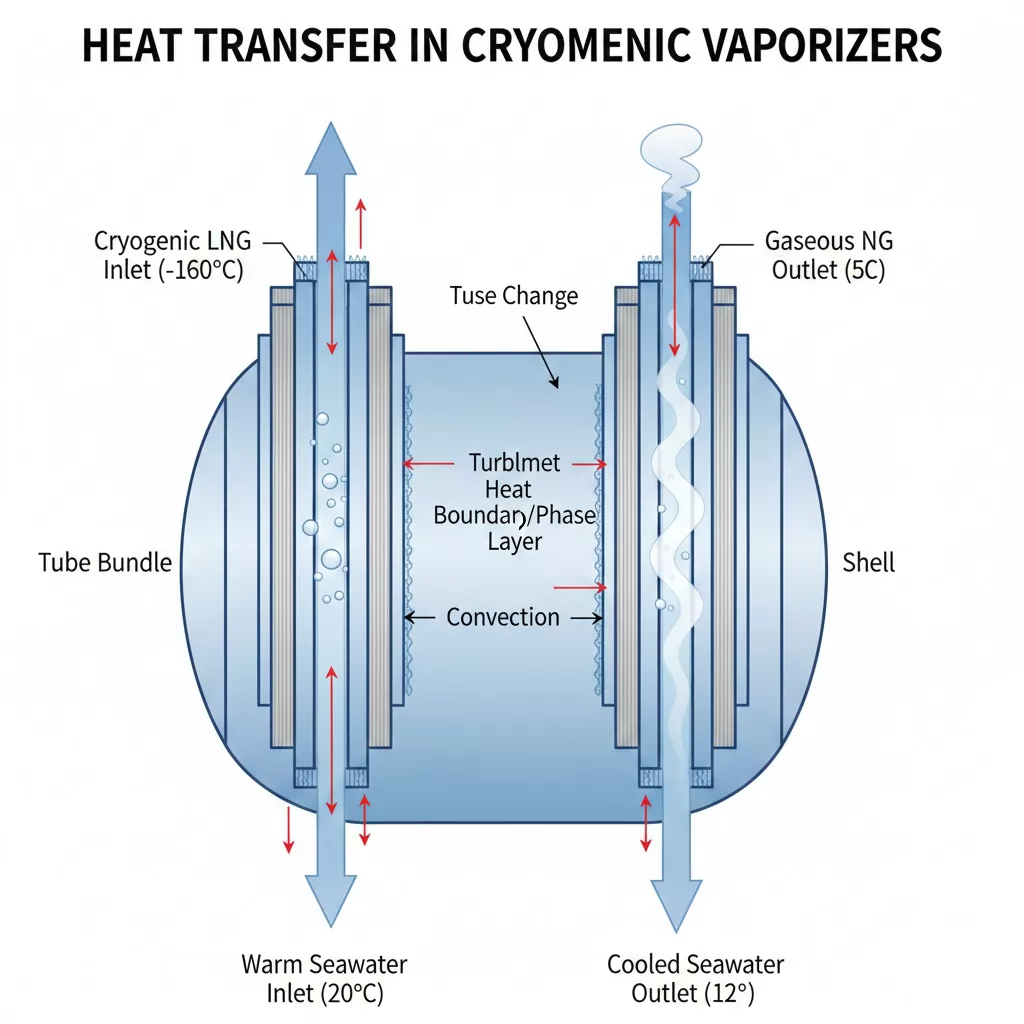
Cryogenic vaporizers function as specialized heat exchangers designed to deliver controlled thermal energy to cryogenic liquids. When heat is transferred to these liquids—stored at temperatures typically below -150°C—they absorb the required latent heat of vaporization and transition into a gaseous state. The effectiveness of this process depends heavily on the vaporizer’s heat-transfer surface area, material conductivity, and the type of heat source supplying the energy. Efficient heat transfer minimizes energy loss, prevents temperature fluctuations, and ensures a stable gas supply for industrial operations.
The vaporization process begins with the cryogenic liquid entering the heat exchanger, where it encounters a warmer surface or medium. Heat is transferred primarily through conduction along the metal tube walls and convection from the external heat source—whether ambient air, steam, hot water, or electric heating elements. As the liquid warms, it first reaches its saturation temperature, then undergoes phase change, absorbing significant latent heat and converting fully into gas. Pressure control and flow-stabilization mechanisms ensure the gas leaves the vaporizer at the correct temperature and delivery pressure required for downstream systems.
Several factors influence heat-transfer performance, including ambient temperature, fin geometry, frost accumulation on air vaporizers, and the thermal responsiveness of the selected heat source. Well-engineered vaporizers manage these variables to maintain consistent output even under fluctuating demand or harsh environmental conditions.
CryoTech’s vaporizer solutions are specifically designed to maximize heat-transfer efficiency through optimized fin structures, high-conductivity materials, and advanced control systems. These engineering enhancements enable rapid, stable vaporization of cryogenic liquids such as nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and LNG, delivering reliable performance for demanding industrial environments.
Cryogenic vaporizers rely on various heat sources to facilitate the vaporization process. Each type is suited to specific applications based on efficiency, cost, and environmental factors. Below are the primary types of heat sources used in cryogenic vaporizers:
These utilize the surrounding air as a heat source, absorbing heat from the air and transferring it to the cryogenic liquid flowing through tubes or coils. Ambient air vaporizers are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, as they require no external energy input. However, their performance can be affected by weather conditions, such as low ambient temperatures or high humidity, which may lead to ice buildup.
These use electric heating elements to directly heat the cryogenic liquid. Electric vaporizers offer precise temperature control and are ideal for applications requiring consistent performance. They are commonly used in controlled environments but may incur higher operational costs due to electricity consumption.
These submerge the cryogenic liquid (often in a coil) in a heated water bath, transferring heat through the water. Water bath vaporizers are highly efficient and suitable for high-volume applications. They are often used in industries where large quantities of gas are needed, such as LNG processing.
These use steam as a heat source, often in a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, to heat the cryogenic liquid. Steam vaporizers are effective for large-scale industrial applications, offering rapid vaporization and high throughput. They are commonly used in facilities with existing steam infrastructure.
These vaporize fluids upstream of a gas flare, often operating at near-atmospheric pressure. Flare vaporizers are specialized for applications in the oil and gas industry, where excess gases need to be safely managed before combustion.
CryoTech offers a range of vaporizers tailored to each heat source, ensuring optimal performance for diverse industrial needs.
Cryogenic vaporizers are complex systems with several critical components that ensure efficient and safe operation. These include:
The core component responsible for transferring heat. It can be finned tubes, coils, or other configurations depending on the heat source and application. The design of the heat exchanger directly impacts the vaporizer's efficiency and capacity.
Cryogenic vaporizers are often insulated to minimize heat loss and maintain the low temperatures of the cryogenic liquid before vaporization. High-quality insulation reduces energy waste and ensures consistent performance.
A system to regulate the pressure at which the gas is delivered after vaporization. This ensures the gas meets the specific requirements of downstream applications, such as industrial processes or pipeline delivery.
CryoTech's vaporizers are designed with advanced components, ensuring durability, efficiency, and precise control for a wide range of applications.
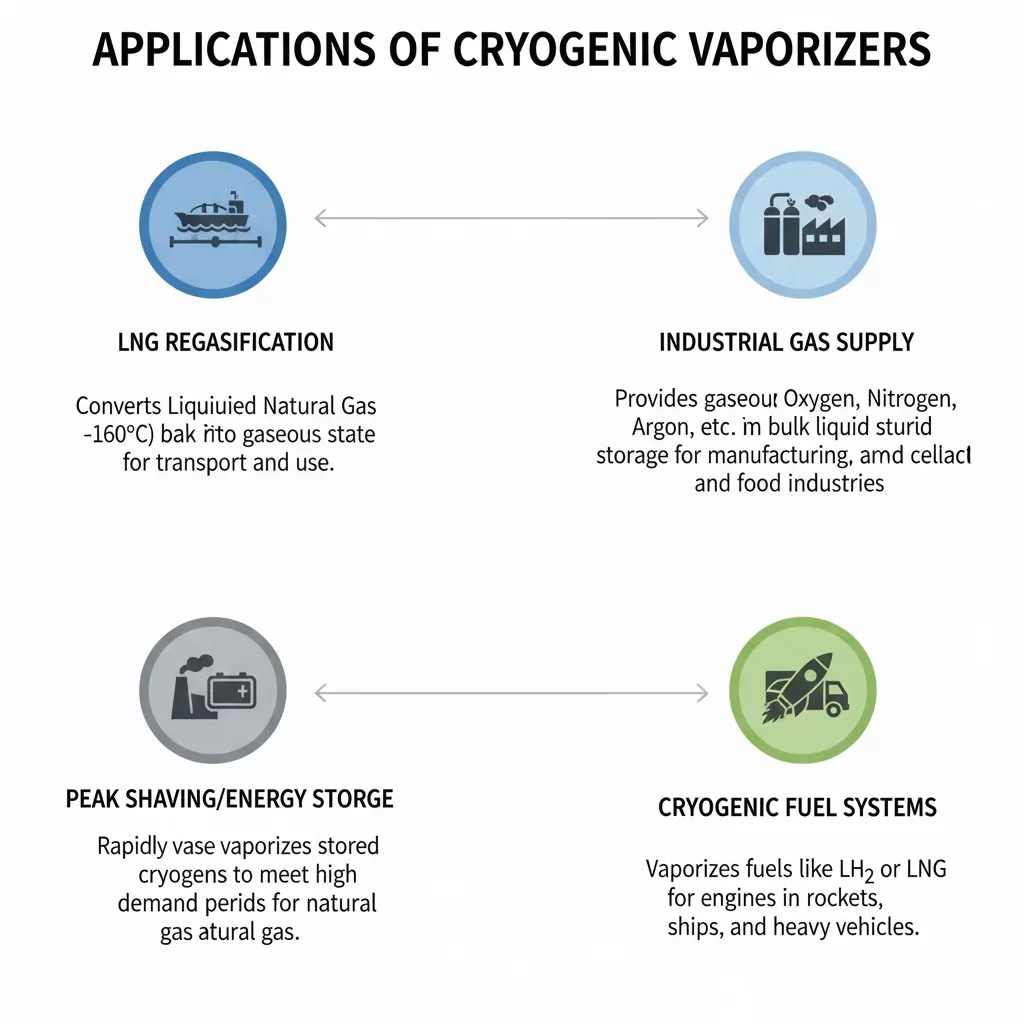
Cryogenic vaporizers support a wide range of industrial and commercial operations where liquefied gases must be efficiently converted to gaseous form. Key application areas include:
CryoTech designs each vaporizer to meet the specific performance demands of these industries, ensuring stable gas output, long-term reliability, and compliance with global safety standards.
When selecting or operating cryogenic vaporizers, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and safety:
Ambient air vaporizers can experience ice buildup on the heat exchanger fins, which can reduce efficiency and require defrosting. Regular maintenance and proper design can mitigate this issue.
Vaporizers are constructed with materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and temperature changes. Stainless steel and aluminum are commonly used for their durability and resistance to cryogenic conditions.
Cryogenic vaporizers must be designed and operated with safety in mind, due to the potential hazards associated with handling cryogenic liquids. Proper training, safety protocols, and equipment design are critical to preventing accidents.
CryoTech prioritizes safety and efficiency, incorporating advanced materials and safety features into its vaporizer designs.
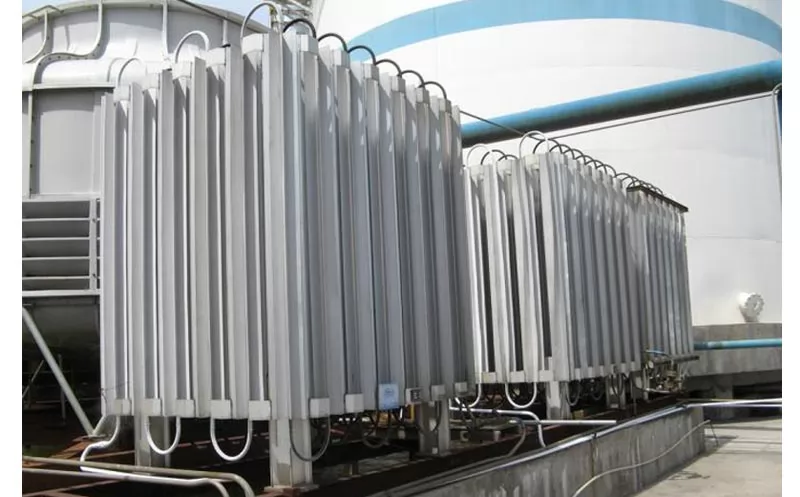

CryoTech stands out as a leader in cryogenic vaporizer technology, offering solutions that combine innovation, reliability, and efficiency. Here's why industries choose CryoTech:
By choosing CryoTech, industries gain access to cutting-edge cryogenic vaporizers that enhance operational efficiency and reliability.
Cryogenic vaporizers play a vital role in transforming cryogenic liquids into usable gases for a wide range of industrial, medical, and research applications. By understanding their heat transfer mechanisms, heat sources, components, and key considerations, industries can select the right vaporizer for their needs. CryoTech's advanced cryogenic vaporizers offer unmatched efficiency, safety, and customization, making them the preferred choice for businesses worldwide.
Whether you're vaporizing LNG for energy production or liquid nitrogen for medical applications, CryoTech provides reliable solutions to meet your demands. Explore CryoTech's product range today to discover how their cryogenic vaporizers can enhance your operations.