From LNG transport to medical gas preservation, cryogenic units play a critical role in modern industrial and scientific processes. But what exactly are cryogenic units, and why are they essential in sectors demanding sub-zero precision?
Defining a Cryogenic Unit: More Than Just Cold
A cryogenic unit is an integrated system designed to achieve, control, and sustain temperatures typically below -150°C (or 123K). These systems are essential where gases must be liquefied, materials must be preserved, or controlled cooling is mission-critical.
Unlike conventional refrigeration, cryogenic systems operate in the realm of liquefied gases such as liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, or LNG (liquefied natural gas).
Breaking Down the System: Core Components of Cryogenic Units
- Cryogenic Tank: Insulated storage for liquefied gases at ultra-low temperatures.
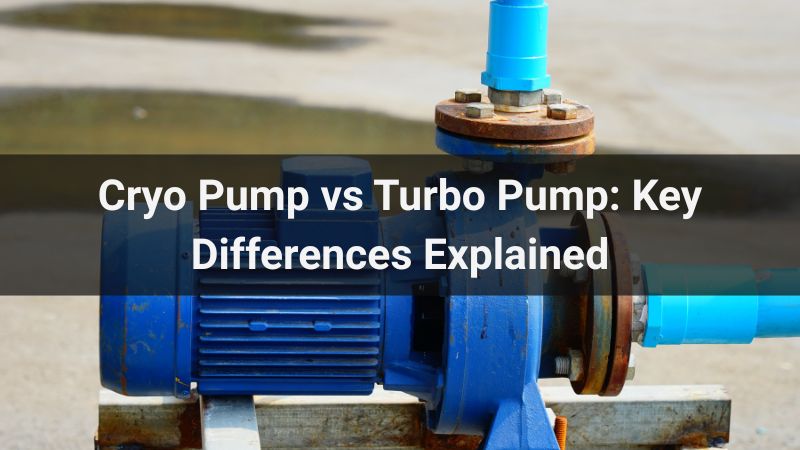
- Cryo Pumps: Specialized pumps designed to transfer cryogenic fluids without excessive heat exchange.
- Vacuum Insulation: Critical for minimizing heat ingress and maintaining thermal efficiency.
- Pressure Control Valves: Ensure safe operation by maintaining internal tank pressure.
- Vaporizer System: Converts cryogenic liquids back into gases for end-use applications.
What Does a Cryogenic Unit Actually Do?
At its core, a cryogenic unit performs three vital tasks:
- Liquefaction: Cooling and condensing gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or natural gas into liquid form.
- Storage: Maintaining these liquids in highly insulated environments to prevent boil-off losses.
- Distribution: Transporting the cryogenic material safely to industrial, scientific, or medical end users.
Cryogenic Units Across Industries: Silent Enablers of Modern Infrastructure
Cryogenic technologies have become indispensable across several key industries:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Energy | LNG storage and regasification terminals |
| Healthcare | Preservation of biological samples, liquid oxygen supply |
| Aerospace | Rocket propellants like liquid hydrogen and LOX |
| Food Industry | Flash freezing and cold-chain logistics |
| Electronics | Superconducting applications and semiconductor cooling |
Choosing the Right Cryogenic Unit: Factors That Matter
Every cryogenic application requires precise system specifications. When selecting a cryogenic unit, consider:
- Type of gas (N₂, O₂, LNG, H₂)
- Required storage capacity and hold time
- Mobility needs: stationary vs. ISO tank trailers
- Operating pressure and temperature range
- Compliance with international standards (e.g., ASME, ISO, GOST)
Consulting a specialized manufacturer with experience in turnkey cryogenic systems can reduce risks and improve system lifecycle efficiency.
Cryo-Tech Solutions: Engineering Cryogenics for the Real World
Cryo-Tech is a leading manufacturer and custom solution provider in cryogenic equipment. From cryogenic tanks and ISO containers to cryo pumps and vaporizers, Cryo-Tech’s systems are engineered for safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance.
Their product portfolio includes:
- Vertical and horizontal LNG storage tanks
- High-capacity ISO tank containers for LPG and LOX
- Mobile cryogenic trailers for transport and refueling
- Cryogenic pump skids with automated PLC control
Explore Cryo-Tech’s full solution suite for your next low-temperature project.
FAQ: Common Questions About Cryogenic Units
- How cold is a cryogenic unit?
- Typically below -150°C, depending on the gas used.
- Are cryogenic units dangerous?
- When properly designed and operated, they are safe. However, cryogenic fluids can cause burns, and pressure buildup must be carefully managed.
- Can cryogenic units be customized?
- Yes. Industrial cryogenic systems are often tailored to specific capacity, gas type, and use-case requirements.




.png)


.png)